Globalization
INTRODCTION
Globalization is one of the most influential phenomena shaping the modern world. It has transformed how countries interact, how economies function, and how cultures influence one another. Through advances in technology, transportation, and communication, the world has become more interconnected than ever before. Goods, services, information, and ideas now move across borders with remarkable speed, creating both opportunities and challenges for societies worldwide.
Globalization is often described as a double-edged sword. On one hand, it promotes economic growth, cultural exchange, and technological advancement. On the other hand, it can deepen inequality, threaten local cultures, and increase economic dependency. Understanding globalization requires examining its origins, dimensions, impacts, and future prospects.
Definition of Globalization
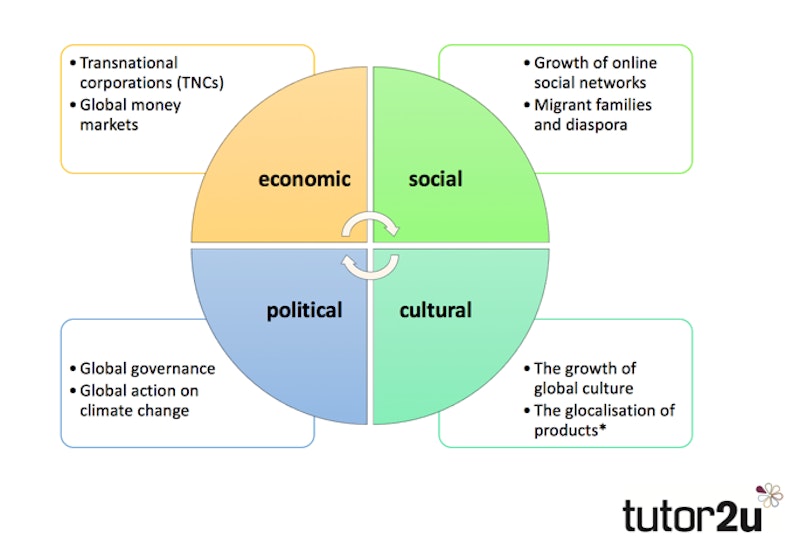
Globalization refers to the process by which countries, economies, cultures, and populations become increasingly interconnected and interdependent. This process is driven by international trade, foreign investment, migration, and the rapid spread of information and technology. Globalization reduces barriers between nations, allowing for greater cooperation and integration at the global level.
It is not limited to economics alone. Globalization affects politics, education, media, health, and even daily lifestyles. As a result, events in one part of the world can have immediate effects on other regions.
Globalization and International Trade
International trade is a cornerstone of globalization. Countries specialize in producing goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage, leading to more efficient resource allocation. Global trade has expanded markets for businesses and provided consumers with a wider variety of products.
Despite these benefits, international trade can negatively affect domestic industries that cannot compete with cheaper imports. This has led to trade disputes, protectionist policies, and debates over fair trade practices.
Cultural Globalization
Cultural globalization refers to the spread of ideas, values, traditions, and lifestyles across borders. Media, entertainment, tourism, and social networks have accelerated cultural exchange, allowing people to experience different cultures without leaving their countries.
While cultural globalization promotes tolerance and mutual understanding, it can also threaten local identities. The dominance of certain global cultures may lead to cultural homogenization, where local traditions and languages gradually disappear.
Social Impact of Globalization
Globalization has reshaped social structures and lifestyles. It has increased mobility, enabling people to migrate for education and employment opportunities. Social media platforms connect individuals across continents, fostering global communities.
However, globalization has also contributed to social inequality. Access to technology and economic opportunities remains uneven, creating a digital divide between and within countries. In some regions, globalization has weakened social cohesion and traditional family structures.
Political Globalization
Political globalization involves the growing influence of international organizations and agreements on national policies. Governments cooperate on issues such as climate change, security, trade, and human rights through global institutions.
While political globalization promotes international stability and cooperation, it can limit national sovereignty. Critics argue that global institutions often favor powerful countries, leaving smaller nations with less influence in decision-making processes.
Technological Globalization
Technology is one of the strongest drivers of globalization. The internet, smartphones, and digital platforms have revolutionized communication, education, and business. Information can now be shared instantly, enabling innovation and collaboration on a global scale.
At the same time, technological globalization raises concerns about data privacy, cybersecurity, and job displacement due to automation and artificial intelligence.
Globalization and Education
Education has been significantly influenced by globalization. Students can access online courses from international universities, participate in exchange programs, and collaborate with peers worldwide. English has emerged as a global language of communication and education.
However, unequal access to quality education remains a challenge. Many developing countries struggle to keep pace with global educational standards, widening the knowledge gap.
